Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI): Everything You Need to Know
Do you spend hours at your computer every day? Are you starting to experience pain in your wrists, hands, or neck? If so, you may be suffering from Repetitive Strain Injury or RSI.
RSI is a condition caused by repetitive motions and can lead to pain, inflammation, and even disability. In this blog post, we will discuss what RSI is, how it is diagnosed, how it is treated, and how poor posture can contribute to the development of this condition.
What is Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Repetitive strain injury, also known as Repetitive Stress Disorder, Repetitive Motion Syndrome or Cumulative Trauma Disorder, occurs from repeated movements over time.
PostureGeek.com Tweet

RSI, also known as Repetitive Stress Disorder, Repetitive Motion Syndrome or Cumulative Trauma Disorder, occurs from repeated movements over time. These injuries can affect any part of the body, including the neck, shoulders and back.
A repetitive strain injury is common among people who perform repetitive motions such as typing on a keyboard or playing an instrument for long periods without proper rest breaks between tasks.
What are the five symptoms of RSI?
The five most common symptoms of Repetitive Strain Injury are:
- Pain,
- Inflammation,
- Numbness or tingling,
- Weakness, and
- Difficulty gripping things.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a recognized health care provider for diagnosis and treatment.
What is the most common type of repetitive strain injury?
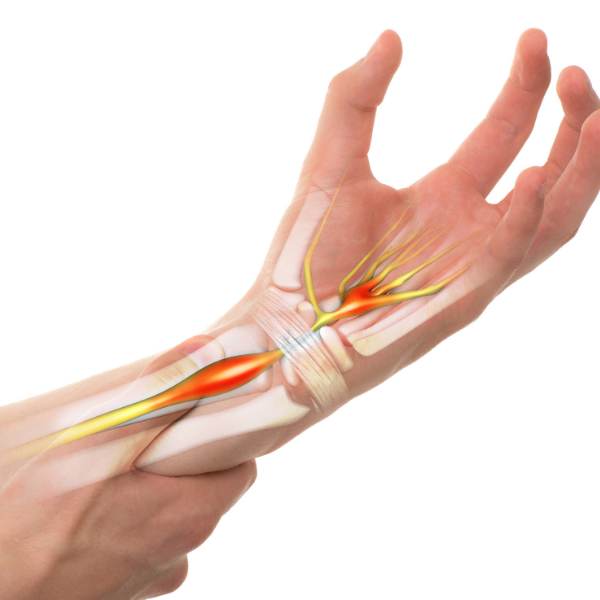
The most common type of Repetitive Strain Injury is carpal tunnel syndrome, which is a condition that affects the wrists and hands.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by repetitive motions that strain the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway in the wrist that houses the median nerve.
When this nerve becomes compressed, it can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hands and wrists.
RSI can also affect other parts of the body such as the neck, shoulders and elbows. Repetitive strain injuries can be caused by various activities, including:
- Typing on a computer keyboard for long periods without proper rest breaks in between tasks or
Playing an instrument for extended periods without taking time to stretch out your muscles before performing again. - Repetitive Strain Injury can also occur from poor posture at work or while using your mobile device (cell phone or tablet).
Common RSIs are:
- Golfer’s elbow
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Tennis elbow
What are Some causes of RSI?
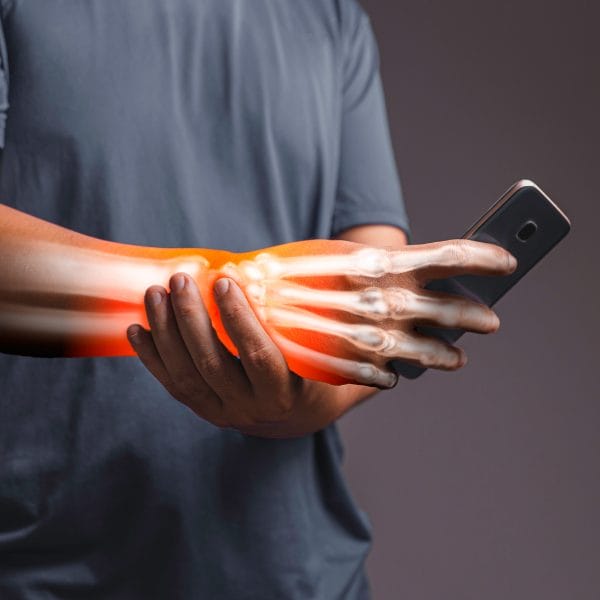

Several factors can contribute to the development of RSI, including:
- Poor posture,
- Performing repetitive motions for long periods without proper rest breaks in between tasks, and
- Working in an environment with poor ergonomics. Poor posture is one of the most common causes of Repetitive Strain Injury.
How RSI is Diagnosed
A doctor can diagnose Repetitive Strain Injury based on the symptoms you are experiencing. The doctor will ask you about the activities you perform daily and will do a physical examination to look for any inflammation or pain in your joints or muscles. They may also order imaging tests such as an X-ray, MRI, or CT scan to rule out other conditions that may be causing your symptoms.locked.
How is Repetitive Strain Injury Treated?
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to the treatment of Repetitive Strain Injury.
PostureGeek.com Tweet

There is no one-size-fits-all approach to the treatment of Repetitive Strain Injury. A variety of treatments that can help relieve the symptoms, including:
- Improve computer workstation.
- Rest, ice, and compression: this is the most common type of treatment for Repetitive Strain Injury. This involves taking a break from the activity causing your symptoms and using ice packs or a cold compress to help reduce inflammation and swelling. You can also wear a compression bandage to help support the affected area.
- Physical Therapies: this may also be recommended to help improve the range of motion and strength in the muscles and joints.
- Performing stretching exercises;
- Taking over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen;
- Wearing a brace or splint to support the affected area.
- In more severe cases, surgery may be required to relieve the pressure on the nerve that is causing the symptoms.
Poor Posture and RSI: How are they related to Each Other?
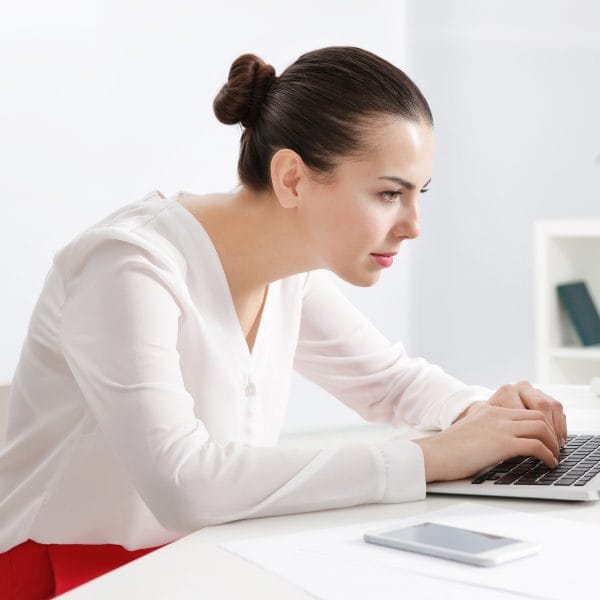

Poor posture is a contributing factor in the development of RSI. Bad posture makes it harder for muscles to do their jobs effectively and can cause pain, discomfort, and injury over time.
A repetitive strain injury is often caused by poor posture because of the constant use of the same joints or tendons for a specific movement, such as typing on a keyboard all day long at work.
How can you prevent Repetitive Strain Injury?
You can do several things to help prevent Repetitive Strain Injury from occurring. Some of these tips include:
- Taking regular breaks throughout the day to move your body and stretch your muscles
- Adjusting your workstation so that it is comfortable for you and fits your body size
- Using a wrist brace or splint to reduce strain on your tendons and ligaments
- Learning how to type correctly with proper posture and wrist placement
- Seek regular complementary treatments from a recognized health care provider
Finally
Repetitive Strain Injury is a serious condition caused by poor posture or repetitive motions. RSI often leads to inflammation, pain, and nerve damage in the arms, hands, legs or feet. Suppose you are experiencing these symptoms at work, whether it’s from sitting slumped over your desk all day long or typing on a computer for hours without breaks. In that case, you may have Repetitive Strain Injury. If symptoms persist or get worse, consult with a recognized health care provider.
PLEASE NOTE
PostureGeek.com does not provide medical advice. This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical attention. The information provided should not replace the advice and expertise of an accredited health care provider. Any inquiry into your care and any potential impact on your health and wellbeing should be directed to your health care provider. All information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical care or treatment.
