Leg Length Discrepancy: What You Need to Know
The body is a mechanism that works tirelessly in its attempt to bring balance and equilibrium to all its functions.
Posture Geek Tweet
Do you have one leg that is noticeably longer than the other? You may have a condition known as leg length discrepancy (or limb length discrepancy). This occurs when there is a difference in the length of your legs. It can cause pain and discomfort and lead to other health problems.
What is Leg Length Discrepancy (LLD)?
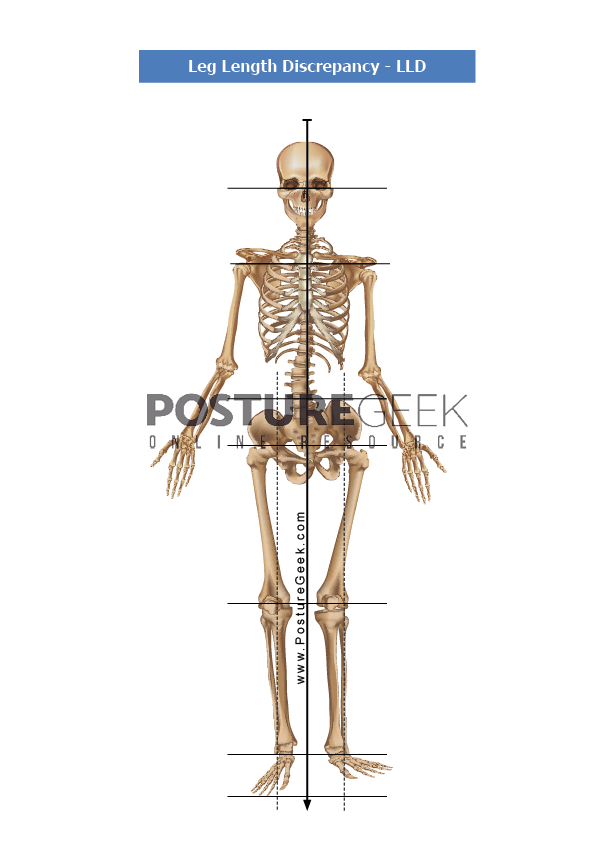
LLD is a state in which one leg is different in length from the other. Research is split on how prevalent this is, with statistics ranging from 40% to 70% of the population.
Limb length difference can be classified as FUNCTIONAL or STRUCTURAL. Many different symptoms are possible if you have it, including back pain, arthritis, scoliosis and more. Limb length discrepancy can occur for many various reasons. It may be present at birth, or it could be the result of an injury or illness.
Our body is a machine that works tirelessly to maintain balance and equilibrium in all of its functions. Unfortunately, when it comes to Limb Length Discrepancy, this mechanism’s attempt to correct the problem may result in more significant inconsistencies and tendencies toward disease rather than ease.
What is the difference between STRUCTURAL and FUNCTIONAL Leg Length Discrepancy?
Structural LLD
It is when there is an actual difference in the length of the femur (thigh bone) and/ or tibia (larger and weight-bearing bone of the lower leg) on either side.
Functional LLD
This can be due to a shift in the relationship of the body’s parts. For example, a lack of range of motion, muscle imbalances, joint contractures (rigidity in the joints), and foot pronation or supination (rolling in or out of the feet) can all contribute to this.
Is Leg Length Discrepancy a problem?
We are the sum of all our parts that influence, and are influenced by its neighbour and as an extension, its neighbours neighbour.
Posture Geek Tweet
There is some disagreement in the research community about how much of a difference in leg length is necessary for it to become a health concern. Some suggest that only a few mm differences can create lower back pain. In contrast, others propose that at least 30-40mm is necessary.
One thing that everyone agrees on, however, is that limb length discrepancy will alter the way your body moves. Changes in mechanics will occur whether the change is minor or glaringly obvious.
For most of us, leg length changes will eventuate into nothing more than the occasional ‘niggle’ or ‘twinge’. Still, for others, lower back pain may be something that no amount of rubbing or cracking can fix.
Visualizing why Leg Length difference can be such an issue
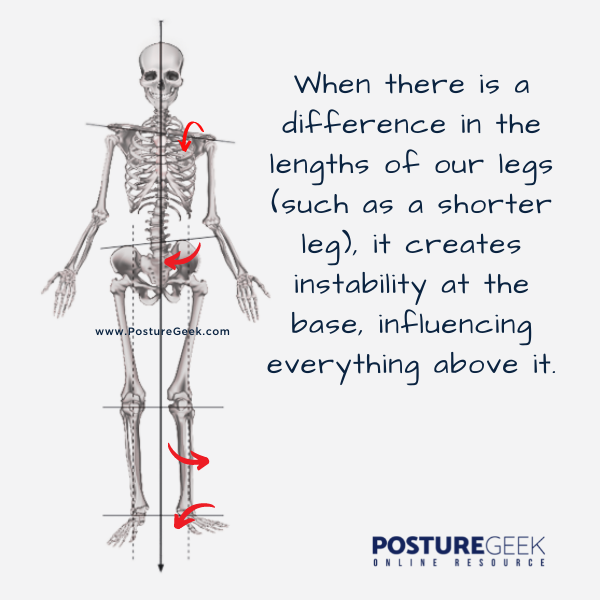
Think of the body in terms of being like a building or any other man-made vertical structure. One element these all have in common is a stable base of support, a secure foundation from which they can build upwards. The human body is no different.
Our relationship to the ground via our feet and lower legs provides a way to support all the elements above – hips, spine, torso, shoulders, neck, and head. This relationship is what gives our bodies the ability to move in an efficient, coordinated, and controlled way.
When there is a difference in the lengths of our legs (such as a shorter leg), it creates instability at the base, influencing everything above it.
The body will do its best to accommodate this change by adjusting our posture and how we move. For example, someone with a Leg Length Discrepancy may start to walk with a limp or may develop lower back pain.
While these compensations help us function in the short term, they can lead to more problems, as structure (or form) can influence function (movement).
Common Causes Of Functional Leg Length Discrepancy
So, how did we get here? What might cause LLD and eventually transform our posture, sitting, and walking habits?
Changes may result from the following factors:
- Joint issues that might cause changes in the spine or leg.
- Dropped arch of the foot.
- A rigid and high arch of the foot.
- Tightness in one hip relative to the other may lead to the pelvis favoring movement in one direction.
- Weakness across a joint – for example, back of the knee creating hyperextension of the lower leg.
- Scoliosis
9 Things That Can Go Wrong If I Have Functional Leg Length Discrepancy?
- Poor postural patterns – an imbalance in the feet, legs, and pelvis can create changes in the spine, rib cage, shoulders, neck, and head.
- Lower Back Pain – is the most common condition associated with LLD.
- Scoliosis: a sideways curvature of the spine that can lead to pain, deformity, and respiratory problems.
- Knee Pain: may result from overcompensation and stress on the knee joint
- Misalignment and/or rotation of the pelvis. What does the pelvis look like? Has this led to sacroiliac joint dysfunction?
- Arthritis
- Severe hip pain – often seen on the longer leg side. Research has explored how the greater the LLD, the greater the pressure in the hip joint along a smaller surface area. That means that load is supported within a concentrated area – leading to more significant wear and tear.
- Myofascial (fascia) restriction and associated pain. What is fascia?
- Physical performance considerations: when placing the body under extreme load or athletic performance. This can be as little as lifting a heavy wheelbarrow in the garden or performing compound weightlifting exercises.
10 causes of Structural Leg Length Discrepancy
- Injuries to the leg or hip joints: bones, muscles, tendons, or ligaments
- Congenital disabilities: abnormalities in the development of the bones or joints
- Diseases that affect bone growth: tumors, osteomyelitis (infection of the bone), and Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
- Congenital leg length inequality: this is when you are born with a difference in your limb lengths
- Developmental: Because of illness or growth plate damage, developmental cases develop over time in the form of a difference in length between the legs.
- Hormonal conditions during fetal development – for example, a deficiency in vitamin A can lead to shortened long bones.
- Infections or illnesses during early childhood that interfere with growth hormone production.
- Injuries to the bone or surrounding tissue can impede growth.
- Amputation of the leg
- Different growth rates in children can also cause leg length discrepancies. If one child’s legs grow faster than the other, it can cause a difference.
Limb length discrepancy diagnosed: how do I know if I have different leg lengths?
The best way to find out is to be assessed by a healthcare professional who can perform a physical examination to measure any limb length discrepancies. Quite often, a complete medical history is necessary to understand the cause of the difference comprehensively.
There are two ways this can be done:
- Measuring from the greater trochanter (bump on the side of the hip) to the medial malleolus (ankle bone) with the person lying down.
- Measuring from the anterior superior iliac spine (top front of the hip bone) to the medial malleolus with the person standing.
Scans may be required to provide a more precise diagnosis.
- X-Ray: this can show bony Leg Length Discrepancies but cannot show any soft tissue differences that may also be present.
- CT scan: this can give a three-dimensional view of any Limb Length Discrepancy and is helpful if you are considering surgery to correct the problem.
What might help with Leg Length Discrepancies?

Treatment for LLD will vary depending on the severity of the discrepancy and the patient’s age.
NON SURGICAL TREATMENT
If the limb length discrepancy is mild and/or you are young, nonsurgical treatment may be an option. This includes:
Observation
Observation is often the first line of treatment, particularly for children, as they are still growing. Your healthcare professional will closely monitor your child to see if the discrepancy gets worse over time.
Physical Therapy
Strengthening and stretching exercises may help to improve muscle balance and flexibility. This can, in turn, help to improve your posture and prevent pain associated with LLD.
Activity Modification
Avoiding activities that put extra stress on the longer leg (running and jumping, for example) can help to prevent pain.
Shoe Lift Or Heel Raises
Wearing a shoe with a built-up heel on the shorter side can temporarily reduce the discrepancy and improve function. This is often only recommended as a short-term solution, however.
Orthotics
Custom-made shoe inserts can level out the pelvis and may provide extra support for the foot, ankle, and lower leg.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
Surgical treatment may be an option if the limb length discrepancy is significant and/or you are older. This includes:
Limb Lengthening Surgery
This is also known as “distraction osteogenesis” or “the Ilizarov technique”. It involves gradual stretching of the bone using an external frame. This method can be used on children who are still growing.
Limb Shortening Surgery
This involves removing a section of bone from the longer limb. It is often only an option if you have an LLD of less than two inches.
Limb Reconstruction Surgery
This type of surgery is usually only an option for children. It involves using artificial materials (such as metal rods) to realign the bones in the limb.
No matter what treatment option you choose, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to ensure that you are making the best decision for your situation.
Finally
Leg Length Discrepancy is a condition that can cause pain and problems with mobility. If you think you may have a limb length discrepancy, it is essential to seek help from a healthcare professional.
There are both nonsurgical and surgical treatment options available, so there is no need to suffer from this situation any longer than necessary. Talk to your recognized health care provider today to determine which treatment option is right for you.
Leg Length Discrepancy can sometimes be painful and debilitating, but help is available. Don’t suffer any longer; seek treatment today.
Updated: October 01, 2022
PLEASE NOTE
PostureGeek.com does not provide medical advice. This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical attention. The information provided should not replace the advice and expertise of an accredited health care provider. Any inquiry into your care and any potential impact on your health and wellbeing should be directed to your health care provider. All information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical care or treatment.
