The Signs and Symptoms Of Flat Back Posture: Understanding Your Posture
Flat Back Posture isn't just an issue for adults; children can also develop it.
PostureGeek.com Tweet
What is Flat Back Posture?
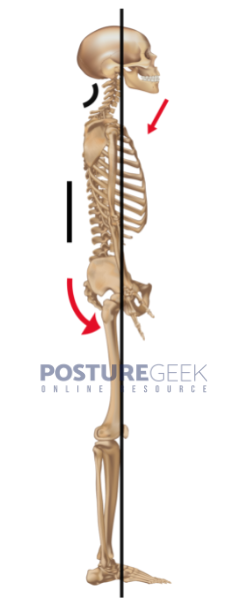
Flat back posture (otherwise known as Flat Back Syndrome) is when the lumbar spine (lower back) has lost its natural curve.
It’s often caused by habitual poor sitting and standing postures. However, it can also indicate other health issues, so this article will discuss the underlying causes of flat back posture and the symptoms.
This posture pattern has been connected with an increased chance of chronic pain, particularly back discomfort and associated spine and disc-related health issues.
On the other hand, this pattern isn’t only about pain; it’s also about how it alters our body structure, making us less healthy than we could be.
Moreover, flat back posture isn’t just an issue for adults; children can also develop it.
For example, which muscles might be tight or shortened? What are the symptoms of a weak muscle? What muscles may be overworking to create muscle fatigue? And what are some factors to consider while assessing maintaining balance while standing?
Causes of Flatback Syndrome
There are many potential causes of flat back syndrome, and it can be caused by problems in any of the following areas:
- The muscles and ligaments that support the spine
- The bones of the spine
- The discs between the vertebrae
- The nerves that come out from the spinal cord
Muscles and ligaments
If the muscles and ligaments that support the spine are weak, this can lead to the spine becoming less stable and the curves in the back becoming flattened. This can be caused by:
- Poor posture – when we slouch or lean our weight forwards, the muscles and ligaments become stretched and over time they may weaken.
- ageing – as we get older, our muscles and ligaments may become less flexible and more prone to injury.
- pregnancy – the extra weight of a baby can put a lot of strain on the muscles and ligaments in the spine.
Bones of the spine
If the bones of the spine are crooked or out of alignment, this can also lead to the spine becoming less stable and the curves in the back becoming flattened. This can be caused by:
- Inherited conditions – some people are born with bones that are less likely to stay in the correct position.
- accidents or injuries – these can cause the bones in the spine to move out of alignment.
- childbirth – during labour, the bones in the spine can move out of alignment as the baby is born.
Discs between the vertebrae
If the discs between the vertebrae are damaged or herniated, this can lead to the spine becoming less stable and the curves in the back becoming flattened. This can be caused by:
- Ageing – as we get older, the discs may become less flexible and more prone to damage.
- Injury – if the discs are damaged, they may bulge or rupture.
- Heavy lifting – if you lift heavy objects regularly, this can put a lot of strain on the discs.
Nerves that come out from the spinal cord
If the nerves that come out from the spinal cord are compressed, this can lead to the spine becoming less stable and the curves in the back becoming flattened. This can be caused by:
- Herniated discs – if a disc bulges or ruptures, it can press on the nerves.
- Spinal stenosis – this is a condition where the spinal cord becomes narrower, which can press on the nerves.
- Bone spurs – these are bony growths that can form on the edges of the vertebrae and press on the nerves.
Symptoms of Flatback Syndrome
The symptoms of flat back syndrome will vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common symptoms include:
- Back pain – this is the most common symptom and it can be caused by problems in any of the areas mentioned above.
- Neck pain – this can be caused by problems in the bones of the spine or the discs between the vertebrae.
- Muscular fatigue – if the muscles in the back are overworking, they can become tired and sore.
- Difficulty standing up straight – you may find it difficult to maintain a straight back.
How do you know if you have Flat Back Posture?
The head, neck, and shoulders display fundamental characteristics of the forward head posture.
PostureGeek.com Tweet
Flat Back posture, like all patterns, comprises elements of several specific alignment issues:
- The head, neck, and shoulders display fundamental characteristics of the forward head posture (found common among many different types of posture).
- At the same time, the middle to upper back presents with a straightening of the thoracic spine, with the lower back’s natural lordosis flattening out.
- Flat Back posture has the tendency to offer only a modest amount of support for the rib cage. This can make the chest collapse downwards, with the possibility of rounded shoulders.
- The pelvis can also demonstrate an excessive movement towards a posterior pelvic tilt (the pelvis tilting under decreasing lumbar lordosis).
- Again, this possibly affects the degree to which the lower back naturally curves, potentially making it difficult to stand upright.
What are some of its characteristics?
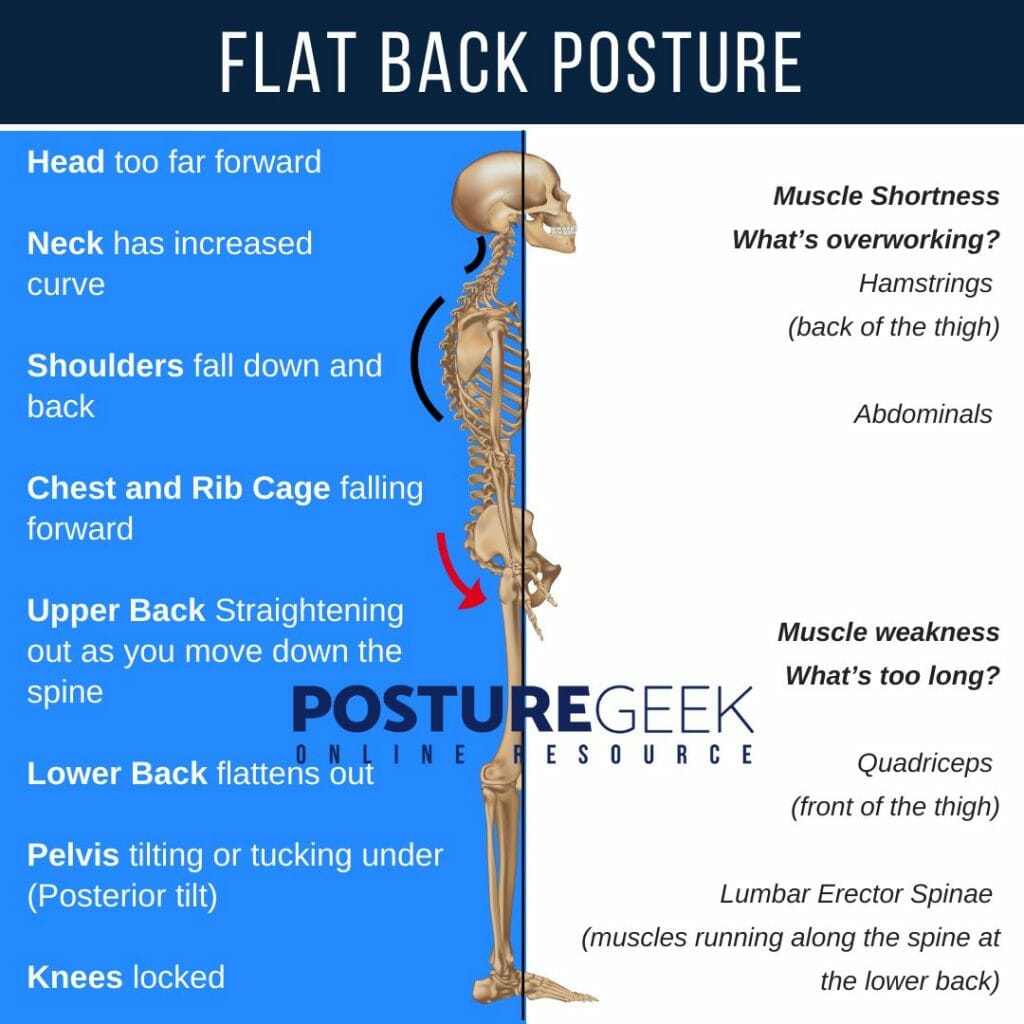
- The head sits is too far forward.
- Neck has an increased curve of the cervical spine.
- Shoulders are falling forward and down, rounding forward.
- The chest and Rib Cage is falling forward.
- Upper Back straightening out as you move down the spine. Removing the upper back natural curve.
- The lower back flattens out, removing the natural lumbar lordosis.
- Pelvis tilting or tucking under (Posterior Pelvis tilt).
- Knees locked.
Which muscles are shortened in flat back posture?
- Hamstrings – back of the thigh
- Abdominal muscles
What muscles are weak in Flat Back Posture?
- Quadriceps – front of the thigh
- Lumbar Erector Spinae – the muscles running along the spine at the lower back
How does Flat Back Posture affect the spine?
The decrease in natural curves means that the spine is more likely to experience increased pressure on areas throughout the spine.
Hips, shoulders, upper back, the lower back can be affected due to the decreased support of their surrounding muscles.
This includes the potential for greater tension on discs and joints put under strain due to the lack of support.
As well as this, it is possible that (in the spine) discs may herniate more easily due to decreased support and increased compression.
Spinal alignment
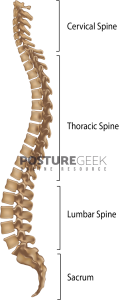
A typical spinal column has an even curve from the neck to the lumbar section. The spinal column bends naturally to allow a person to sit up, stand up and walk comfortably. The curvature of the spine grows greater as you descend from the top of your head until reaching your lower back.
Your bottom should be slightly curved inward while standing, stretched flat when sitting, and touching the ground while walking.
This natural curve in your spine provides you with abdominal support. In addition, it protects this delicate weight-bearing structure against injury or pain that may affect function across all aspects of life for years into your future!
When presenting with changes, your spine curves abnormally – depending on which part of your spine is impacted, it’s either flat or hunched or slouched.
What are some considerations for Flat Back Posture?
One consideration when examining is the shortening and tightening of muscles. This may lead to muscle spasms and tenderness in the back and/or neck region.
Another consideration when assessing is the weakening of muscles, such as the quadriceps, iliopsoas, lumbar erectors, and abdominal muscles.
This weakness may lead to fatigue when performing physical activity that would otherwise be easy to achieve.
It can also be caused by lower back pain, including iliopsoas bursitis, iliopsoas tendonitis, or lumbar disc disease.
If you’re experiencing pain and discomfort and think your posture might be contributing to it, seeking professional assistance may be a good idea.
FLATBACK POSTURE CAN LEAD TO SOME DAY-TO-DAY ISSUES:
- Loss of energy and mood swings
- Impaired breathing and sleeping comfortably
- Limited physical activity
- Tension, stiffness, spasms, or aches in the back or neck region
What are some medical-related spinal issues related to Flat Back Posture?
Degenerative Disc Disease
In some people, progressive disc deterioration may cause a loss in height in the front of the spine. This is because the vertebrae begin to lean forward as discs degenerate, decreasing lumbar lordosis. People may also feel discomfort as a result of disc disease or misalignment.
Lumbar Post Laminectomy Syndrome
Suppose you have previously undergone a laminectomy or other lumbar surgery to decompress spinal nerves for stenosis. In that case, you may be at risk of developing a flat lumbar spine. In addition, as your Lumbar lordosis is reduced, spinal instability may be caused by these methods in certain situations.
Vertebral Compression Fractures
A compression fracture is often the result of weak bones. For example, the spine may develop a break or cracks, leading to height loss in the thoracic and lumbar spine. This can lead to back pain and a rounding of the thoracic spine, a vital characteristic of this posture pattern.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a degenerative disease of the spine that causes stiffness and arthritis throughout the whole spine. In addition, some patients with AS report an increase in thoracic kyphosis or lumbar lordosis and forward positioning of the spine’s posture, including a worsening of the flat lower back.
Ways to prevent flat back posture caused by day-to-day misuse.
This posture pattern may be prevented by stretching muscles such as the pectoralis major (upper chest), posterior deltoid (back of the shoulder), and erector spinae (low back muscles).
Exercises to improve flat back postures may include:
- Stretches that target pectoralis major, posterior deltoid, iliopsoas (front hip muscle), and erector spinae
- Postural awareness to bring attention to any poor posture patterns.
- Exercises that target the abdominals and lower back muscles
- Scapular stabilization exercise to stabilize shoulders and upper body
- Activities, which may involve stretches and movement of joints against resistance from gravity
Further considerations?
Tightness of the abdominals and hamstrings, coupled with possible weakness in the quadriceps, increases the chance of the pelvis tilting (tucking) under and the lower back flattening out or being placed in an excessively lengthened state.
This has the direct potential of placing ligaments and/or discs of the lumbar spine (lower back) at risk of injury or damage.
Like all patterns, work towards improving the lower back natural curve to improve posture. You can start this process by improving the position of the pelvis.
For example, if the pelvis is too tucked under (posterior pelvic tilt), you may need:
- The pelvis to tip (or angle) forward slightly
- To understand your lumbar spine (lower back) placement?
- A balanced pelvis makes sure the pelvis and hips can be free enough to offer the lumbar spine the opportunity to move into a slight curve.
In Closing
Flat Back Posture can affect your health by changing how you stand and sit. Therefore, it’s essential to know the signs so that you can make adjustments before it becomes a chronic condition, which may lead to pain or other problems.
This pattern is not always caused by poor sitting habits but rather is due to tight muscles around the pelvis or weak abdominals that push forward on the rib cage. Avoid issues by sitting in a chair with proper support, lifting and carrying objects with good posture, and exercising to strengthen the core.
Note
Use these considerations as a starting point, but always remember to refer to a qualified practitioner who has the skills to assist in improving your posture.
References
