The Importance of the Erector Spinae Muscles: An Overview
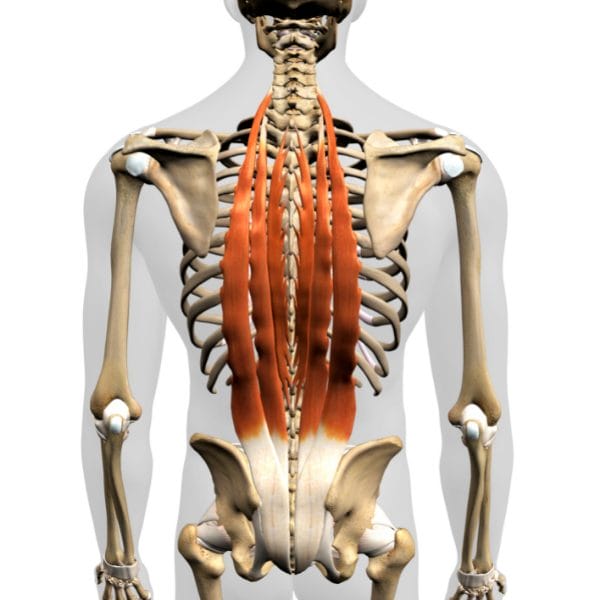
The Erector Spinae muscle group are three distinct, deep back muscles that run along either side of the spine. They extend from the sacrum and hips (pelvis) all the way up to the base of the skull (Occipital bone). These muscles are located on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, covering the lumbar (lower back), thoracic (middle back), and cervical (neck) regions.
Anatomy of the Erector Spinae Muscles
The Erector Spinae muscles (also known as the spinal erectors) are a group of muscles that support and move the spine. They consist of three muscles: the Iliocostalis, Longissimus, and Spinalis. While these muscles collectively don’t cover the entire spine, they play important roles in specific regions.
- Iliocostalis: This muscle runs along the sides of the spine, from the hips to the ribs and neck. It supports the lumbar vertebrae (lower back), thoracic vertebrae (mid-back), and cervical vertebrae (neck).
- Longissimus: Positioned in the middle, the Longissimus muscle extends from the hips to the skull. It runs parallel to the spine, providing support and movement to the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical regions.
- Spinalis: The Spinalis muscle lies closest to the spine, running from the sacrum to the skull. While it doesn’t cover the entire spine, it primarily supports the thoracic vertebrae and helps maintain the natural curve of the spine.
Together, these muscles, play vital roles in supporting the lumbar spine, thoracic spine, and cervical spine regions. They provide stability, enable movements like extension and rotation, and contribute to overall back health.
By understanding the basic anatomy of the spinal erectors, we can appreciate their importance in maintaining a healthy spine and promoting proper posture.
Erector Spinae Muscles function

The main function of the Erector Spinae muscles is to extend (keep upright) and rotate the spine. These muscles also help to maintain the natural curvature of the spine, which is essential for proper posture.
Some specific functions include:
- Keeping the spine upright: The Erector Spinae work together to keep the spine in an upright position, even when the body is at rest.
- Supporting the spine during movement: These muscles help support the spine during movements like side bending (lateral flexion), twisting (rotation), and reaching, which can put significant strain on the back.
- Assisting with breathing: The Erector Spinae muscles help expand the ribcage during deep breathing, which is vital for delivering oxygen to the body.
In addition to these functions, the Erector Spinae muscles also play a crucial role in maintaining balance and stability in the body. These muscles work in conjunction with other muscles in the back and the core and lower body muscles to keep the body stable during movements like walking, running, and jumping.
Potential injuries and imbalances
The Erector Spinae muscles have a vital role in supporting and moving the spine (Vertebral Column). However, neglecting these muscles or performing improper movements can lead to potential injuries and imbalances.
Injuries and imbalances
When the Erectors are subjected to excessive strain or repetitive stress, they can experience injuries such as strains or spasms. These injuries can cause pain and discomfort, limiting your range of motion and overall functionality. Moreover, muscular imbalances in the Erector Spinae muscles, where certain muscles are stronger or tighter than others, can further contribute to postural deviations and increased risk of injury.
Importance of proper form and gradual progression
To minimize the risk of injuries and imbalances, it is crucial to maintain proper form during exercises that target the Erector Spinae muscles. Focus on using appropriate techniques, engaging the correct muscles, and avoiding excessive load or overexertion. Gradual progression in intensity and weight is also essential for the muscles to adapt and strengthen gradually.
Importance of the Erector Spinae Muscles to Posture

Good posture, and just as importantly posture awareness, is essential for maintaining a healthy spine – reducing the risk of back pain and injury. The Erector Spinae muscles play a crucial role in maintaining proper alignment by:
- Providing stability: These muscles stabilize the spine and keep it upright, which is an essential element for good posture.
- Supporting the natural curvature of the spine: The natural curvature of the spine is important for maintaining ‘good’ posture. By their attachment to spinous and transverse processes the Erector Spinae muscles help support this curvature.
- Preventing hunching: Hunching or slouching can strain the back significantly and lead to pain and injury. The Erector muscles work to avoid hunching and to promote good posture.
In addition to the benefits of good posture, there are several other reasons why keeping the Erector Spinae muscles strong and healthy is important. These include:
- Reduced risk of injury: Strong Erector Spinae muscles can help protect the spine from harm during physical activity or daily tasks.
- Improved athletic performance: The Erector Spinae muscles play a crucial role in many athletic movements, such as jumping and throwing, and a strong back can improve overall athletic performance.
- Better breathing: As mentioned earlier, the Erector Spinae muscles assist with breathing by expanding the ribcage, improving oxygen delivery to the body, and promoting overall health and well-being.
Postural deviations

Importance of the Erector Spinae Muscles to Posture
As mentioned above, maintaining good posture is crucial for a healthy spine, and the Erector Spinae muscles play a significant role in supporting proper alignment. Weak or imbalanced Erector Spinae muscles can contribute to postural deviations, including kyphosis, lordosis, and scoliosis.
Postural deviations explained
Kyphosis is characterized by an excessive upper back rounding, leading to a hunched posture. Lordosis refers to an exaggerated inward curve of the lower back, causing the pelvis to tilt forward and the abdomen to protrude. Finally, scoliosis involves a sideways curvature of the spine, leading to an asymmetrical posture.
The role of the Erector Spinae muscles
When the Erector Spinae muscles are weak or imbalanced, they may fail to provide adequate support to the spine, exacerbating postural deviations. Strengthening these muscles can help improve postural alignment and reduce the severity of these conditions.
Benefits of addressing postural deviations
Correcting postural deviations enhances your appearance, promotes better spinal health, and reduces the risk of discomfort or pain associated with poor posture. In addition, by strengthening the Erector Spinae muscles and practising proper alignment, you can minimize the strain on your spine and promote overall postural balance.
Importance of targeted exercises
Incorporating exercises targeting the Erector Spinae muscles and a comprehensive approach to overall back health can help address postural deviations. In addition, by working on strengthening and balancing these muscles, you can improve your posture and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Remember, it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist, to assess and develop an individualized plan to address postural deviations and strengthen the Erector Spinae muscles effectively.
By understanding the impact of weak or imbalanced Erector Spinae muscles on postural deviations and taking steps to address them, you can promote better spinal alignment and enhance your overall posture and well-being.
Prevention and management of Erector Spinae

Exercises alone aren’t the only aspect to consider when it comes to maintaining the health of the Erector Spinae muscles. Prevention and management strategies are equally important in promoting strength and avoiding injuries or imbalances.
Proper form and gradual progression
When performing exercises that target the Erector Spinae muscles, it is crucial to maintain proper form. This ensures that the muscles are engaged correctly and reduces the risk of strain or injury. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine, avoiding excessive rounding or arching, and engaging the muscles throughout the movement. Additionally, gradually progressing the intensity and weights of exercises allows the muscles to adapt and strengthen over time.
Stretching and mobility exercises
Incorporating stretching and mobility exercises specific to the back can help maintain flexibility and prevent muscle tightness. For example, dynamic stretches, such as cat-cow and trunk rotations, can help warm up the Erector Spinae muscles before exercising. Additionally, static stretches like child’s pose and seated spinal twists can be performed to improve flexibility and relieve muscle tension.
Rest and recovery
Allowing sufficient rest and recovery time is vital for the health of the Erector Spinae muscles. Adequate rest allows the muscles to repair and rebuild, preventing overuse injuries and promoting overall muscle health. Ensure you incorporate rest days into your exercise routine and prioritize quality sleep for optimal recovery.
Body mechanics and ergonomics
Beyond exercise, being mindful of your body mechanics and ergonomics during daily activities can significantly contribute to the health of the Erector Spinae muscles. Maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting objects, ensuring alignment and avoiding excessive strain on the back. Use ergonomic equipment and adjust workstations to support a neutral spine position.
Seeking professional guidance
While exercises and self-care practices are valuable for maintaining the health of the Erector Spinae muscles, it’s essential to recognize the benefits of consulting a healthcare professional. Seeking guidance from experts can provide individualized assessment and expert advice to enhance your efforts.
Assessment and personalized guidance
A qualified healthcare professional can thoroughly assess your back health, including the strength, flexibility, and balance of your Erector Spinae muscles. In addition, they can identify any specific weaknesses, imbalances, or movement patterns that may contribute to discomfort or injuries. Based on this assessment, they can provide personalized guidance and exercises tailored to your unique needs and goals.
Proper exercise technique
Working with a healthcare professional ensures that you perform exercises targeting the Erector Spinae muscles with correct form and technique. They can guide you through proper body alignment, breathing techniques, and modifications to prevent further strain or injury. This professional oversight can maximize the effectiveness of your exercises while minimizing the risk of setbacks.
Injury prevention and management
A healthcare professional can offer specialized strategies to prevent and manage such issues if you have a history of back pain, previous injuries, or existing conditions. In addition, they can provide insights into movement modifications, additional exercises, and therapeutic techniques to promote healing and enhance the strength and resilience of your Erector Spinae muscles.
Long-term support and progress tracking
Working with a professional allows for ongoing support and monitoring of your progress. They can adjust your exercise routine as needed, challenge you appropriately, and track your improvements over time. This accountability and guidance can motivate you and ensure you’re on the right track toward optimal back health.
Remember, the expertise and guidance of a healthcare professional are invaluable when it comes to addressing specific concerns, ensuring safe and effective exercise, and optimizing your journey to a healthy back.
By consulting a physical therapist or qualified fitness trainer, you can benefit from their knowledge and experience, receive individualized care, and gain the confidence to overcome challenges and achieve your back health goals effectively
In Conclusion
In conclusion, the Erector Spinae muscles are an essential group of muscles that play a crucial role in supporting and protecting the spine, enabling movement, and maintaining good posture. By incorporating exercises that target these muscles specifically, practicing good posture and engaging in core-strengthening exercises, you can keep your back strong and healthy and reduce the risk of back pain and injury.
PLEASE NOTE
PostureGeek.com does not provide medical advice. This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical attention. The information provided should not replace the advice and expertise of an accredited health care provider. Any inquiry into your care and any potential impact on your health and wellbeing should be directed to your health care provider. All information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical care or treatment.
