Everything You Need to Know About the Rotator Cuff: Anatomy, Injuries, and Treatment Options
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. These muscles and tendons are responsible for rotating the arm in different directions. They are also important in keeping the arm stable in the shoulder socket.
PostureGeek.com Tweet

The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. These muscles and tendons are responsible for rotating the arm in different directions.
They are also important in keeping the arm stable in the shoulder socket. Unfortunately, the rotator cuff can be injured in several ways, including falls, accidents, and sports injuries.
What is the anatomy of the rotator cuff?
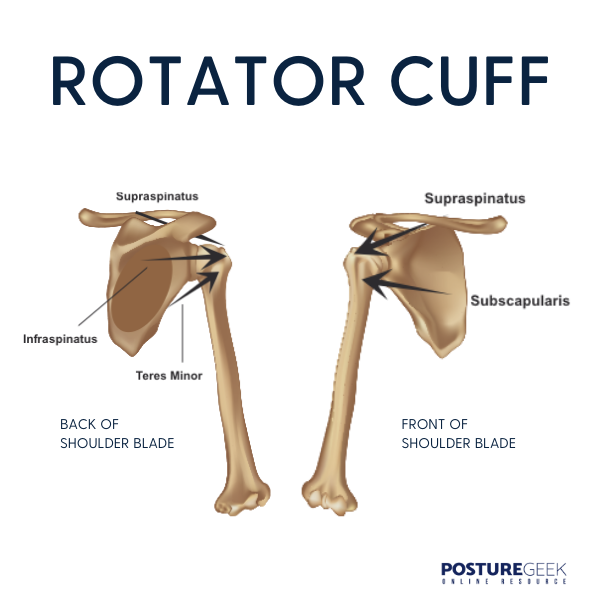
The rotator cuff is made up of four muscles and their corresponding tendons. These muscles are the:
- supraspinatus,
- infraspinatus,
- teres minor, and
- subscapularis.
The muscles and tendons attach to the shoulder blade and the upper arm bone. These muscles help rotate the arm in different directions and keep the arm stable in the shoulder socket.
What are common rotator cuff injuries?
Rotator cuff injuries are common among athletes and people who perform overhead activities.
PostureGeek.com Tweet

Rotator cuff injuries are common among athletes and people who perform overhead activities. These muscles and tendons can be injured by overuse or sudden force.
Common injuries include:
Tendon tear
Tendon tears are the most common rotator injury. They can occur from a sudden force, such as in a fall or accident, or overuse. They can be partial or full-thickness tears. Partial-thickness tears are less severe than full-thickness tears and may not require surgery. Full-thickness tears are more severe and may require surgery.
Rotator cuff impingement
Impingement is a condition in which tendon is pinched between the shoulder blade and upper arm bone. This can occur from overuse or from a fall or accident. Impingement usually occurs in athletes who do many overhead activities, such as throwing, swimming, and tennis.
Inflammation
Inflammation occurs when the rotator cuff muscles and tendons become inflamed. It can occur from overuse or injury, such as impingement or bursitis. Inflammation is usually treated with rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication. Sometimes steroid injections are also used.
Bursitis
Bursitis is a condition in which the bursa becomes inflamed. Bursitis is usually treated with rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication. Sometimes steroid injections are also used.
Who is more likely to suffer a rotator cuff injury?
A shoulder injury can occur in anyone. Still, people who are more likely to suffer an injury include:
- Athletes who do a lot of overhead activity, such as throwing, swimming, and tennis
- People who perform repetitive tasks with their arms, such as typing or using a cash register
- Older adults who have been inactive for a long time
What are the symptoms of rotator cuff injuries?
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of injury. Common symptoms include:
- shoulder pain that limits specific movements
- shoulder stiffness
- difficulty raising the arm overhead
- weakness in the arm
- issues lying on the damaged side
- popping or clicking sound in the shoulder
What are the treatment options?
Try to keep your weight evenly distributed when standing or walking. This will create a more stable foundation.
PostureGeek.com Tweet

The treatment options for rotator cuff injuries vary depending on the type of injury. The most common treatment fincludes rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication. If the injury is severe, you may need surgery. Surgery is often recommended for tendon tears that are full-thickness tears.
Treatments for injuries include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy and other allied health practitioners can help improve the rotator cuff muscles’ range of motion and strength.
- Cortisone injections: Cortisone injections are injected directly into the muscles to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: Surgery is often recommended for tendon tears that are full-thickness tears. Surgery may involve repairing the rotator cuff muscles and tendons or removing the damaged tissue.
- Brace: A brace may be recommended to help keep the arm in a neutral position and improve shoulder stability.
- Exercises: Exercises that target the rotator cuff muscles can help improve strength and range of motion in the shoulder. These exercises are often prescribed after surgery.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation, pain, and swelling in the rotator cuff muscles and tendons.
What are some complications of a rotator cuff injury?
Complications of rotator cuff injuries can include:
- Shoulder stiffness
- Shoulder weakness
- Reduced range of motion
- Pain
- Persistent inflammation
- Scar tissue formation
- Tendon or muscle tear
- Bursitis
- Arthritis of the shoulder joint
How long does it take to recover from rotator cuff injuries?
It can take a few weeks to a few months to recover from rotator cuff injuries. The length of time it takes to recover depends on the type and severity of the injury. Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication are usually the first line of treatment for injuries. If the damage does not improve with treatment, steroid injections may be used. Surgery may be necessary for more serious tears. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment plan for you.
Finally
Rotator cuff injuries can be caused by a variety of things, such as overuse, accidents, or inflammation. Common treatments for rotator cuff injuries is rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication. However, if the injury is severe, surgery may be necessary. Rotator cuff exercises can help improve strength and range of motion in the shoulder. Talk to your health care provider about the best treatment plan for you.
PLEASE NOTE
PostureGeek.com does not provide medical advice. This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical attention. The information provided should not replace the advice and expertise of an accredited health care provider. Any inquiry into your care and any potential impact on your health and wellbeing should be directed to your health care provider. All information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical care or treatment.
